
Spokeswoman of the Foreign Ministry Le Thi Thu Hang on June 24 emphasised Vietnam’s demand for the relevant parties to not take any action that further complicates the situation in the East Sea, but contribute to the maintenance of peace and stability in the waters.

Deputy Spokesman of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs Doan Khac Viet underlined Vietnam’s objection to China’s recent fishing ban while detailing Vietnam’s viewpoints on several issues related to the East Sea at the ministry’s regular press conference on April 29.

The Party Central Committee’s Commission for Information and Education opened a press centre serving the upcoming 13th National Party Congress at a ceremony in Hanoi on January 22.

The East Sea is a semi-closed expanse of water abutting seven countries - Vietnam, China, the Philippines, Malaysia, Brunei, Indonesia, and Singapore. It is not only crucial for their development but also a strategic link in several international maritime routes. The sea holds several strategic benefits that are eyed by global powers.
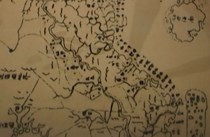
The Vietnamese people have left their footprints on the Hoang Sa (Paracel) and Truong Sa (Spratly) islands since ancient times. Historical evidence proves the country’s sovereignty over the two archipelagos, especially through ancient bibliographies.

The East Sea plays a vital role in Vietnam’s defence, security, and economy. The Vietnamese Party and State have issued important policies on East Sea issues, to protect the country’s independence, sovereignty, unity, and territorial integrity, maintain a peaceful environment, and ensure security, social order, and safety for national construction and defence.